Digestate Resource Recovery Options!
Currently there are various digestate resource recovery options available along with their potential end usage, because of the different evolving resource recovery technologies.
Biosolids and digestate have long been used to agricultural lands to take advantage of the nutrients and micronutrients of these products, with the aim to increase soil fertility or structure. But recently, a wide range of resource recovery options has evolved from the digestate beyond this conventional agricultural use. Some of the drivers behind this evolution are mainly search for renewable fuel sources, reducing greenhouse gases and reducing transportation cost to the suitable application sites. Also there are some disadvantages associated with land application such as high nitrogen content with potential of ammonia and nitrate pollution, high dilution requirements, needs for supplementary nutrient addition to create a balanced fertilizing feed etc.
At present, the focus is on complete nutrient recovery and creating value added products from digestate. In recent practices digestate is separated in to two different fractions- fibre and liquor. These fractions have different nutrient profile with different potential uses and potential markets.
The water content of digestate can be reduced through dewatering process. The solid resulted from dewatering process has reduced volume and thus has reduced trucking and fuel cost for its handling and disposal. Moreover, this solid can be used for composting to create a value added product for soil amendments. The composting product has fertilization benefits as well. The dewatered solid can be dried up further to make it more suitable for further energy recovery options like gasification and pyrolysis. These processes produce syngas that can be used as an alternative source of energy. In addition, pyrolysis produces char; which has potential to be used as soil amendments and fertilizer. Supplementary nutrient can also be added to the dried digestate product to create a balanced fertilizer.
The liquid generated from dewatering process known as centrate, can also be utilized further. This liquor is very high in nutrients like ammonia and phosphorus. Both of these nutrients can be precipitated from digestate liquor as struvite that can later be transformed into an organic fertilizer. As equal amounts of ammonia and phosphate are used in struvite production and digestate is relatively rich in ammonia, a significant quantity of ammonia can still be recovered through ammonia precipitation from the left-over liquor. Moreover, digestate liquor can be treated through any biological wastewater treatment process like MBR, SBR etc. which generates a high quality reusable effluent. The treated digested liquor can be used as process water or as irrigation water.
With various evolving resource recovery technologies from digestate, before selecting any treatment/ recovery technology, the overall plant economy should also be kept in mind. The end use of the final products and theirs existing market should also be considered.
Different Digestate Resource Recovery Technologies and End Use Options:
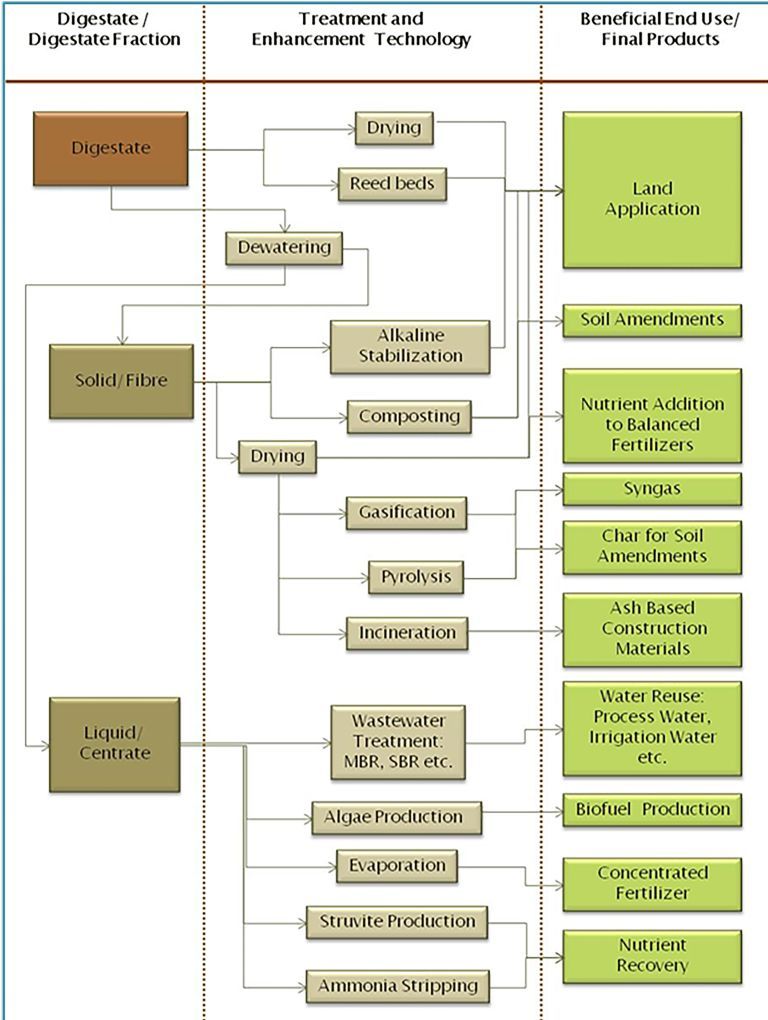
Digestate resource recovery technologies and end use diagram
Go to the Recent Advances in Anaerobic Digestion!
Discover More on Digestate Resource Recovery!
Go Back to The EcoAmbassador Home!
Total Visits to Site:
